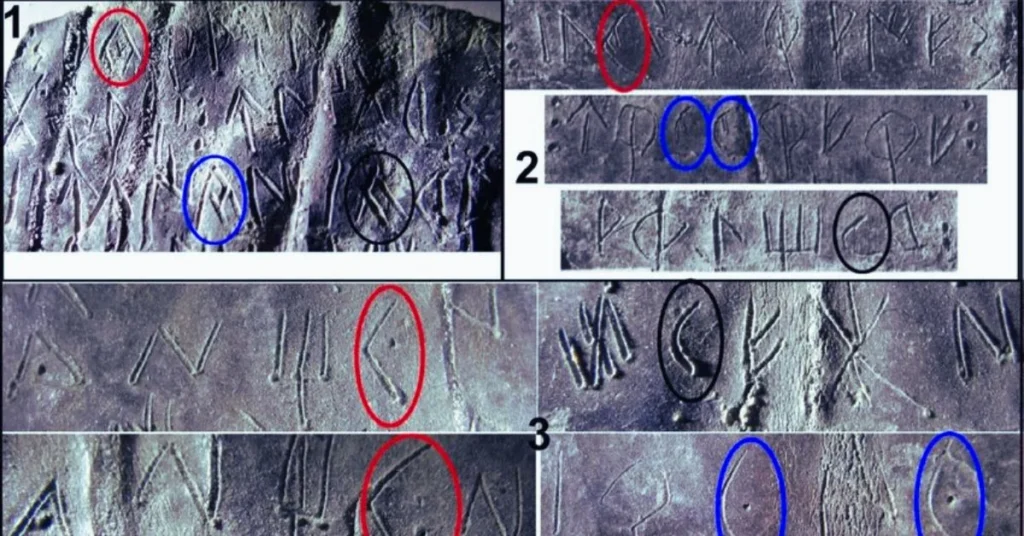
The concept of “trialidad” (tri-unity) in the context of “plomos” (lead tablets or inscriptions) is an intriguing aspect of textual analysis, particularly in historical and epigraphic studies. This term refers to the existence and interaction of three distinct but interconnected textual variants or versions within a set of inscriptions. The study of trialidad helps scholars understand the evolution of texts, the interplay between different linguistic or cultural influences, and the dissemination of ideas across time and geography.
What Are Plomos?
Plomos, or lead tablets, are ancient inscriptions typically made on thin sheets of lead. These tablets have been found in various archaeological sites, often serving as records of transactions, curses (defixiones), or religious dedications. The durability of lead as a material has allowed these inscriptions to survive through the centuries, providing valuable insights into the linguistic, social, and cultural aspects of the ancient societies that produced them.
Textual Variants: Definition and Importance
Textual variants are differences in wording, phrasing, or structure found in multiple versions of a text. These variations can arise from:
- Geographical Spread: As texts are copied and disseminated, regional linguistic features and scribal practices can introduce changes.
- Temporal Evolution: Over time, language and writing styles evolve, leading to updates and modifications in texts.
- Cultural Interactions: Contact with other cultures and languages can influence the content and form of inscriptions.
Studying these variants is crucial for reconstructing the history of a text, understanding the context of its production, and identifying the influences that shaped its evolution.
Trialidad: Threefold Variants
Trialidad refers to the presence of three interrelated textual variants within a set of plomos. This phenomenon can be analyzed through:
- Linguistic Analysis: Examining the language, grammar, and syntax of the inscriptions to identify regional dialects, linguistic changes over time, and influences from other languages.
- Paleographic Study: Analyzing the handwriting styles, letter forms, and inscription techniques to date the tablets and understand the scribal traditions.
- Contextual Interpretation: Understanding the historical, cultural, and social context in which the plomos were produced, including religious practices, legal systems, and societal norms.
Case Studies and Examples
Several notable examples of trialidad in plomos highlight the diversity and complexity of these inscriptions:
- Iberian Plomos: Inscriptions from the Iberian Peninsula often show variants in the use of Iberian, Latin, and Punic languages, reflecting the multicultural interactions in ancient Hispania.
- Curse Tablets (Defixiones): Greek and Latin curse tablets found across the Roman Empire demonstrate how local dialects and regional practices influenced the wording and structure of these texts.
- Religious Dedications: Inscriptions dedicated to deities, found in different regions, exhibit variations in religious terminology, ritual descriptions, and invocations, revealing localized religious practices and beliefs.
Methodological Approaches
To effectively study trialidad in plomos, scholars employ a combination of methodologies:
- Comparative Textual Analysis: Comparing different versions of a text to identify common elements and unique variants.
- Epigraphic Survey: Conducting comprehensive surveys of inscriptions from various sites to compile and categorize textual variants.
- Interdisciplinary Research: Integrating insights from linguistics, history, archaeology, and cultural studies to provide a holistic understanding of the inscriptions.
Conclusion
The study of trialidad in plomos offers a rich field of inquiry for understanding the complex interactions between language, culture, and society in the ancient world. By examining the threefold textual variants in these lead inscriptions, scholars can gain deeper insights into the processes of textual transmission, cultural exchange, and the historical contexts that shaped these fascinating artifacts.
FAQs
1. What is trialidad in the context of plomos?
Trialidad refers to the presence of three distinct but interconnected textual variants within a set of plomos (lead tablets or inscriptions). These variants help scholars understand the evolution of texts, the interplay between different linguistic or cultural influences, and the dissemination of ideas over time and geography.
2. What are plomos?
Plomos are ancient inscriptions typically made on thin sheets of lead. They have been found in various archaeological sites and often serve as records of transactions, curses (defixiones), or religious dedications. The durability of lead has allowed these inscriptions to survive through the centuries, providing valuable insights into ancient societies.
3. Why are textual variants important?
Textual variants are important because they reveal differences in wording, phrasing, or structure across multiple versions of a text. These differences can arise from geographical spread, temporal evolution, and cultural interactions. Studying these variants helps reconstruct the history of a text, understand its context, and identify the influences that shaped its development.
4. How do scholars analyze trialidad?
Scholars analyze trialidad through:
- Linguistic Analysis: Examining language, grammar, and syntax to identify regional dialects and linguistic changes.
- Paleographic Study: Analyzing handwriting styles, letter forms, and inscription techniques to date the tablets and understand scribal traditions.
- Contextual Interpretation: Understanding the historical, cultural, and social context of the plomos.
5. Can you provide examples of trialidad in plomos?
Yes, several examples illustrate trialidad:
- Iberian Plomos: Show variants in Iberian, Latin, and Punic languages, reflecting multicultural interactions in ancient Hispania.
- Curse Tablets (Defixiones): Greek and Latin curse tablets found across the Roman Empire demonstrate regional linguistic influences.
- Religious Dedications: Inscriptions dedicated to deities from different regions exhibit variations in religious terminology and practices.